
Study of Charmonium formed in proton-antiproton interactions

Charmonium particles (bound states of charm and anticharm quarks) have been discovered and extensively studied in electron-positron collider machines. This approach is limited by two factors:
· Only states with the same quantum numbers of the photon (JPC = 1- -) can be formed (such as J/Y and Y’), and accurate measurements can be made also for states directly connected via radiative transitions (such as: hc , chi 0, chi 1, chi 2);
· Initial-state radiation in the electron-positron annihilation causes a spread in the total c.m. energy that does not allow a direct measurement of the narrow width of several Charmonium states.
Both difficulties can be overcome with experiments where Charmonium is formed in proton-antiproton annihilations, to the expense of selecting the events from a large background.
This road was taken by the experiments CERN-ISR-R704, Fermilab-E760 and its successor E835.
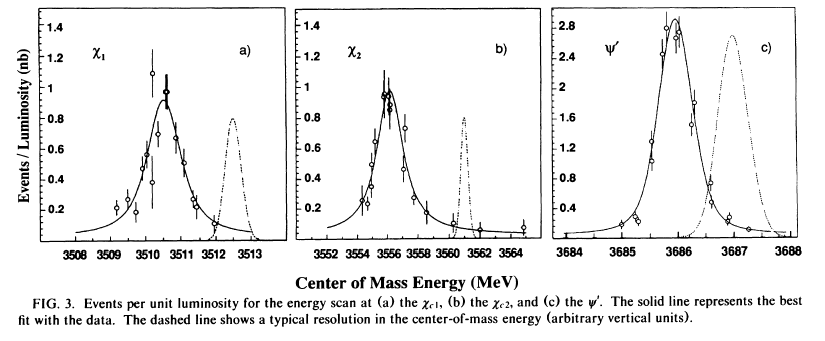 E760
(Fermilab, Ferrara, Genova, Irvine, Northwestern, Penn State, Torino
Collaboration) used antiprotons stored in the Antiproton Source of Fermilab,
brought into collision with an ultrasonic jet of hydrogen crossing the
accumulator pipe. Emphasis was placed on the detection of photons and
electrons/positrons. Data were collected in the early 90's, providing accurate
measurements of mass and width of several Charmonium states, and first evidence
for the 1P1(hc) spin singlet state.
E760
(Fermilab, Ferrara, Genova, Irvine, Northwestern, Penn State, Torino
Collaboration) used antiprotons stored in the Antiproton Source of Fermilab,
brought into collision with an ultrasonic jet of hydrogen crossing the
accumulator pipe. Emphasis was placed on the detection of photons and
electrons/positrons. Data were collected in the early 90's, providing accurate
measurements of mass and width of several Charmonium states, and first evidence
for the 1P1(hc) spin singlet state.
link to the web page of the experiment Fermilab-E835 and of E760